Learning objectives:
1. Developing visual brand identity
· Translating brand identity into something visual
· Important factors and elements in creating a visual brand identity
· How to keep your visual brand identity consistent in relation with time and place?
2. Touchpoints & consistency
· How to keep the brand identity consistent over different touchpoints?
· Related case studies
3. How does the visual brand identity affect the relation to your audience?
· How does the public respond to the visual brand identity?
· Case studies
-------------------------------------------
1. Developing visual brand identity
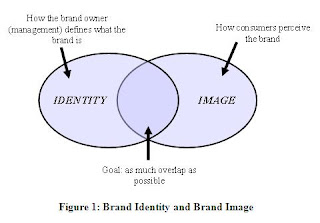
1.1 How to translate brand identity to some visual
Visual brand identity meaning gain audience's perception by visualising your actions to show them your personality. So what we can do to visualise brand identity to make audience remember immediately when they see company's signs?
Imagine when we visit a website, we will be influenced by colour of texts, font, size, layout where you are able to perceive impression with the company. This impression is actually very important as it contributes to the decision making process whether we use their products.
So first thing that a company needs to do to visualise its brand identity is to determine who is the audience and how to deliver values to these targets. The targets could be separated by age, gender, culture, habit, social influence, etc. Then the company knows what to do to transfer expected messages to the audience (Jacqueline Thomas, 2015)
It is necessary to keep communication channels emotional and simple. People tend to be easier to remember the more specific thing which can be able to meet audience's dreams than the exaggerating but empty statement. This requires value proposition that only the company can provide for its customers. Another point is to keep things simple from the font, logo, website. They shouldn't be so completed which makes audience distracted and misunderstood. The company's signs must be avoided confused. It should be consistent in fonts and colours. It is very be wise to use many fonts at the same time and no particular colour (Jacqueline Thomas, 2015). Logo must have five factors: simple, aesthetic, memorable, usable, timeless (Giuseppe Liuzzo, 2014)
There is one question that how often shall we tell story? In my opinion information should be updated and recalled very frequently. Many people have asked themselves why companies have paid a big number to advertise on TV which is seen as getting smaller result than other ways. It is actually a good way to step by step gain recognition of audience about the products. Why they throw lots of money just to repeat some slogan all the time. Because this brings long-run awareness from audience and get them remember unconsciously.
Elements of visual identity (Giuseppe Liuzzo, 2014)
Logo - FACE
Colors - PERSONALITY
Types - VOICE
Textures, Patterns, Treatments - DRESS
All the elements should speak the same language.
Source:
Jacqueline Thomas, 20 Actionable Tips to Build a Winning Visual Brand Identity 2015, https://designschool.canva.com/blog/20-easy-tips-build-visual-brand-identity/
Giuseppe Liuzzo, How to Design Strong Brand Identities 2014, http://www.slideshare.net/liuzzodesign1/how-to-design-strong-brand-identities
1.2 Keep visual brand identity consistent by time and place
It is not easy to keep brand identity remain the same as it is in certain countries. Even Pepsi, Honda, McDonald's had struggling in foreign culture, language, and demand.
HOW TO REACH THE CERTAIN MARKET?
Even big companies who are well-known and successful in many places need to be careful when enter the new markets. The company should focus on 1 or 2 markets at the time. Market research never becomes more serious than this to learn about the local regulations, customers' demands, social trends, etc.
It is very important to keep core values of the company meanwhile adapting with the local values by fixing the messages. For example, McDonald's and KFC have different menus in different countries like Asian menus have rice and different in India where people don't eat pork or beef.
TRANSLATION FOCUS
Good translation is essential. Once companies decide to jump into new places, they need natives to translate the messages to reach its objectives. In real there are many examples of failing to translate messages to other languages.
e.g. KFC with slogan "finger lickin' good" became "eat your fingers off" when translating to Chinese
Pepsi had slogan "come alive with Pepsi generation" was mistranslated as "Pepsi brings your ancestors back from the dead" in 1963 -1967
Honda was forced to change brand Honda Fitta to Honda Jazz in EU markets as they released that it was translated in Norway and Sweden as female genitalia
CULTURE DIFFERENCES
Writing in The Journal of Business Research, Mark Cleveland and Michel Laroche contend that: “More than any other factor, culture is the prime determinant of consumers’ attitudes, behaviours and lifestyles, and therefore, the needs that consumers satisfy through the acquisition and use of goods and services.”
Source:
Christian Arno, Adapting Brands for Different Cultures 2013, http://www.chiefoutsiders.com/blog/bid/94476/Adapting-Brands-for-Different-Cultures
Come Alive!, Snopes webpage 2011, http://www.snopes.com/business/misxlate/ancestor.asp
2. Touchpoints & consistency
Figure. Brand Touchpoint Matrix
The horizontal axis plots touchpoints from those often experienced during shorter periods of time (and that doesn’t require too much involvement from the customer) to longer term interactions and relations.
The vertical axis tell us if the touchpoint has more mass media properties (reaches lots of people) or if it’s more suited for personal interactions (easier to create a personal experience) (Jonas Persson)
Case study: Starbucks
1. Starbucks's cup
2. Word of Mouth
3. Store exterior and location
4. Customer service
5. Assortment
6. Sitting area
7. tasty
8. Merchandising
9. Social Responsibility
Source:
Jonas Persson, brandtouchpoint webpage, http://brandtouchpointmatrix.com
3. How does the public respond to the visual brand identity?
Consistency is a big element to get audience remember the brand. Some elements help company's signs easily be recognised by audiences:
Symbolism
Colour Theory
Text Content
Ultimately
"Consumers often can identify the brand sponsor of an ad with a quick glance, even before the logo is glimpsed and without reading any of the text. A beach scene in a beer ad elicits Corona; a mother and a child in a soup calls out Campbell's. This suggests that nonverbal elements play a prominent role in branding." (Phillips, B, McQuarrie, E, and Griffin, W.G, 2014)
Case:
This is an example of SKYY vodka that audience don't need to notice a lot to know it's Skyy products with hyper colour and glossy visual
Source:
Phillips, B, McQuarrie, E, and Griffin, W.G. Journal of Psychology and Marketing 2014. "How Visual Brand Identity Shapes Consumer Response", p225
Figure. Honours Year Blog: How Visual Brand Identity Shapes Consumer Response, 2014, http://leithhonoursyear.blogspot.fi/2014/12/how-visual-brand-identity-shapes.html
Cass Fanara, Visual Communication: Creating an Effective Brand Identity, 2015, https://digitalmarketingroom.wordpress.com/2013/03/24/visual-communication-creating-an-effective-brand-identity/